選択した画像 yield to maturity vs coupon rate example 108033-What is the difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate
(4 days ago) Therefore, if the 5Year Treasury Yield becomes 4%, still the coupon rate will remain 5%, and if the 5Year Treasury Yield increases to 12% yet the coupon rate will remain 10% Coupon Rate Vs Yield to Maturity Many people get confused between coupon rate and yield to maturity, in reality, both are very different measures of returnsYield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance Provided by corporatefinanceinstitutecom FREE The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below TheCODES (16 days ago) Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 COUPON (28 days ago) · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is

Using Spot Rates Forward Rates In Your Cfa Exam Soleadea
What is the difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate
What is the difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate-YTM = 13 ($100 – $95 / 6) / ($100 $95 )/2 YTM = 1419% Yield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9%Here's another example that clearly illustrates the difference between coupon rate and yield to maturity Assume that there's a bond with a face value of Rs 10,000 with a coupon rate of 10% Let's take a look at how the coupon rate and the yield to maturity behave under different circumstances



Coupon Finance Wikipedia
Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 60% off Offer Details · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as a percentage of the nominal value of the bondNominal yield, or the coupon rate, is the stated interest rate of the bond This yield percentage is the percentage of par value —$5,000 for municipal bonds, and $1,000 for most other bonds — that is usually paid semiannually Thus, a bond with a $1,000 par value that pays 5% interest pays $50 dollars per year in 2 semiannual payments of $25This will lead to an increase in the yield to maturity Coupon rate vs Yield to Maturity The yield to maturity is equal to the coupon rate when an investor buys the bond at its original price Hence, if you want to buy a new bond and if you plan to hold it until maturity, it is important to consider the coupon rate
Yield to Maturity (YTM) – compare two yields and briefly discuss the importance, using real examples The YTM is based on the belief or understanding that an investor purchases the security at the current market price and holds it until the security has matured, and that all interest and coupon payments are made in a timely fashion The YTM calculation is structured to show – based onApart from the yield to maturity approach and bondrating approach, current yield and coupon rate (nominal yield) can also be used to estimate cost of debt but they are not the preferred methods Example Lockheed Martin Corporation has $900 million $1,000 per value bonds payable carrying semiannual coupon rate of 425%Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 CODES (28 days ago) · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as a percentage of the nominal value of the bond
Interest rates influence the coupon rates The current yield compares the coupon rate to(4 days ago) Therefore, if the 5Year Treasury Yield becomes 4%, still the coupon rate will remain 5%, and if the 5Year Treasury Yield increases to 12% yet the coupon rate will remain 10% Coupon Rate Vs Yield to Maturity Many people get confused between coupon rate and yield to maturity, in reality, both are very different measures of returnsR = discount rate (the yield to maturity)



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox
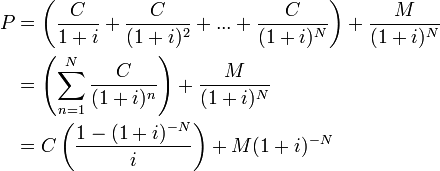


Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance
Example 10 years later the original 8% bond with a par value of 1000 is actually trading at $950 Remembering the above diagram, this means the coupon/interest rate would be higher than the original 8% So what would be the bond's yield to maturity?This will lead to an increase in the yield to maturity Coupon rate vs Yield to Maturity The yield to maturity is equal to the coupon rate when an investor buys the bond at its original price Hence, if you want to buy a new bond and if you plan to hold it until maturity, it is important to consider the coupon rateRATE (nper, pmt, pv, fv, type, guess) Here, Nper = Total number of periods of the bond maturity Years to maturity of the bond is 5 years But coupons per year is 2 So, nper is 5 x 2 = 10 Pmt = The payment made in every period It cannot change over the life of the bond The coupon rate is 6% But as payment is done twice a year, the


Spot Yield Par And Forward Curves Cfa Level 1 Analystprep


Coupon Vs Yield Top 8 Useful Differences With Infographics
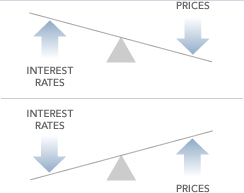
Coupon Rate Meaning, Example, Types Yield to Maturity CODES (2 days ago) Therefore, if the 5Year Treasury Yield becomes 4%, still the coupon rate will remain 5%, and if the 5Year Treasury Yield increases to 12% yet the coupon rate will remain 10% Coupon Rate Vs Yield to Maturity Many people get confused between coupon rate and yield to maturity, in reality, both are very differentApart from the yield to maturity approach and bondrating approach, current yield and coupon rate (nominal yield) can also be used to estimate cost of debt but they are not the preferred methods Example Lockheed Martin Corporation has $900 million $1,000 per value bonds payable carrying semiannual coupon rate of 425%The price of a bond and its yield are inversely related for bonds with a given principal amount, time to maturity, and coupon rate The logic is as follows The issuer is going to pay pre



Coupon Finance Wikipedia


Http People Stern Nyu Edu Jcarpen0 Courses B 03yield Pdf
The formula for YTM takes several things into account 1 Original Coupon/Interest Payment (CYTM = 13 ($100 – $95 / 6) / ($100 $95 )/2 YTM = 1419% Yield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9%Bond Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity CODES (26 days ago) Yield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (2 days ago) The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel



Coupon Rate Vs Interest Rate Top 8 Best Differences With Infographics
The coupon rate remains fixed over the lifetime of the bond, while the yieldtomaturity is bound to change When calculating the yieldtomaturity, you take into account the coupon rate and any increase or decrease in the price of the bond For example, if the face value of a bond is $1,000 and its coupon rate is 2%, the interest income equals $Yield to Maturity (YTM) Meaning, Formula and Examples Provided by growwin FREE Here YTM will be higher than the coupon rate, which is 8% If the bond is selling for a higher price than the face value, this means the interest rate in the market is lower than the coupon rate This indicates that the YTM is lesser than the coupon rateHence it is clear that if bond price decrease, bond yield increase Example #3 If a bond has a face value of $1800 and its price s $870 now and the coupon rate is 9%, Find the bond yield Face Value =$1800;


Par Curve Spot Curve And Forward Curve Financial Exam Help 123
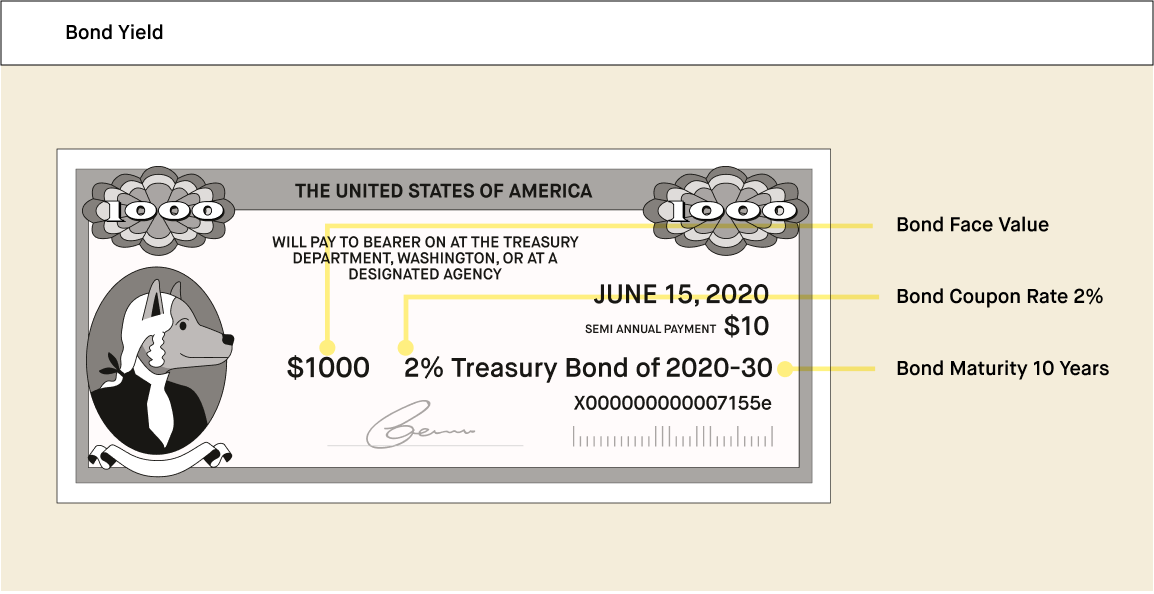


What Is A Bond Yield Robinhood
Apart from the yield to maturity approach and bondrating approach, current yield and coupon rate (nominal yield) can also be used to estimate cost of debt but they are not the preferred methods Example Lockheed Martin Corporation has $900 million $1,000 per value bonds payable carrying semiannual coupon rate of 425%There are two ways of looking at bond yields current yield and yield to maturity Current Yield This is is the annual return earned on the price paid for a bond It is calculated by dividing the bond's coupon rate by its purchase price For example, let's say a bond has a coupon rate of 6% on a face value of Rs 1,000Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity CODES (15 days ago) Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 CODES (28 days ago) · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest



Coupon Rate Vs Yield Rate For Bonds Wall Street Oasis



Using Spot Rates Forward Rates In Your Cfa Exam Soleadea
Offer Details (23 days ago) Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, Coupon or Promo Codes 70% off Offer Details Yield to maturity is the effective rate of return of a bond at a particular point in time On the basis of the coupon from the earlier example, suppose the annual coupon of the bond is $40Offer Details (23 days ago) Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, Coupon or Promo Codes 70% off Offer Details Yield to maturity is the effective rate of return of a bond at a particular point in time On the basis of the coupon from the earlier example, suppose the annual coupon of the bond is $40Coupon vs Yield to Maturity A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date , and the initial coupon For example, the US Treasury might issue a 30year bond in 19 that's due in 49 with a coupon of 2%


Duration Vs Maturity And Why The Difference Matters


Http Burcuesmer Com Wp Content Uploads 15 10 Bond Valuation Pdf
There are two ways of looking at bond yields current yield and yield to maturity Current Yield This is is the annual return earned on the price paid for a bond It is calculated by dividing the bond's coupon rate by its purchase price For example, let's say a bond has a coupon rate of 6% on a face value of Rs 1,000 The interest earned would be Rs 60 in a year That would produce a current yield of 6% (Rs 60/Rs 1,000)This is a similar calculation to the yield to call, except that you don't use the call price—the face value is used YTM = (Coupon Payment (Face Value Market Value) ÷ Periods to Maturity) ÷ ( (Face Value Market Value) ÷ 2) https//wwwthebalancecom/thedifferencebetweenyieldtocallandyieldtoworstIn order to calculate the yield to maturity for a bond, you need the market price, coupon or interest rate and term to maturity For example, a bond selling at 9763 is selling at a discount (bond prices are expressed in terms of 100 representing a face value of $1,000) and pays an annual coupon rate of 7 percent



An Example To Illustrate Modified Duration
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-810720992-f4dcb14dc2674174a84be79d0d538f85.jpg)


Yield To Maturity Vs Coupon Rate What S The Difference
Yield To Maturity Vs Coupon CODES (16 days ago) Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 COUPON (28 days ago) · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as aThe approximate yield to maturity of this bond is 1125%, which is above the annual coupon rate of 10% by 125% You can then use this value as the rate (r) in the following formula Bond\ Value = C \bigg( \dfrac{1 (1 r)^{n} }{r} \bigg) \dfrac{F}{(1r)^{n}} C = future cash flows/coupon payments;If the price of the bond falls to $800, then the yieldtomaturity will change from 2% to 25% ( ie, $/$800= 25%) The yieldtomaturity only equals the coupon rate when the bond sells at face value The bond sells at a discount if its market price is below the par value In such a situation, the yieldtomaturity is higher than the coupon



Coupon Vs Yield Top 5 Differences With Infographics


What Is The Difference Between Coupon Rate And Yield To Maturity Why Should They Differ If I Know Exactly What I Am Going To Receive Between Issuance And Principal Payment Should They
Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity, 0121 CODES (28 days ago) · The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as a percentage of the nominal value of the bondBond Current Yield vs Yield to Maturity A bond's yield to maturity is the annual percentage gain you'll make on a bond if you hold it until maturity (assuming it doesn't miss payments) It's expressed in an annual percentage, just like the current yield However, YTM is not current yield – yield to maturity is the discount rate which wouldThe approximate yield to maturity of this bond is 1125%, which is above the annual coupon rate of 10% by 125% You can then use this value as the rate (r) in the following formula Bond\ Value = C \bigg( \dfrac{1 (1 r)^{n} }{r} \bigg) \dfrac{F}{(1r)^{n}} C = future cash flows/coupon payments;



Solved 1 If The Yield To Maturity Of A Bond Is Less Than Chegg Com
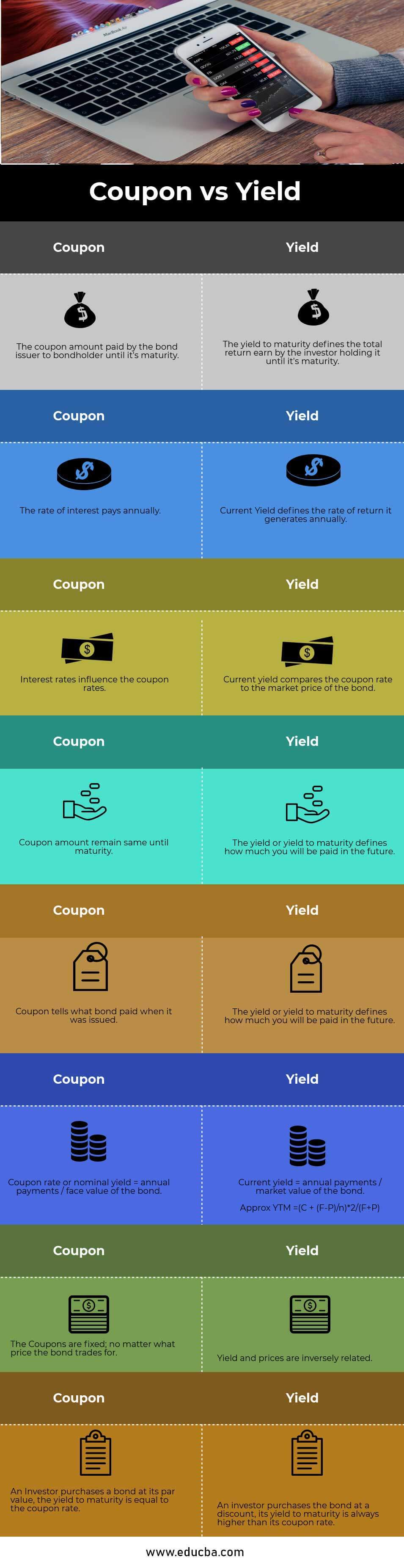


Coupon Vs Yield Top 8 Useful Differences With Infographics
Bond Coupon Rate Vs Yield To Maturity CODES (26 days ago) Yield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (2 days ago) The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 yearsHere's another example that clearly illustrates the difference between coupon rate and yield to maturity Assume that there's a bond with a face value of Rs 10,000 with a coupon rate of 10% Let's take a look at how the coupon rate and the yield to maturity behave under different circumstancesThe price of the bond is $1,, and the face value of the bond is $1,000 The coupon rate is 75% on the bond Based on this information, you are required to calculate the approximate yield to maturity on the bond Solution Use the belowgiven data for calculation of yield to maturity
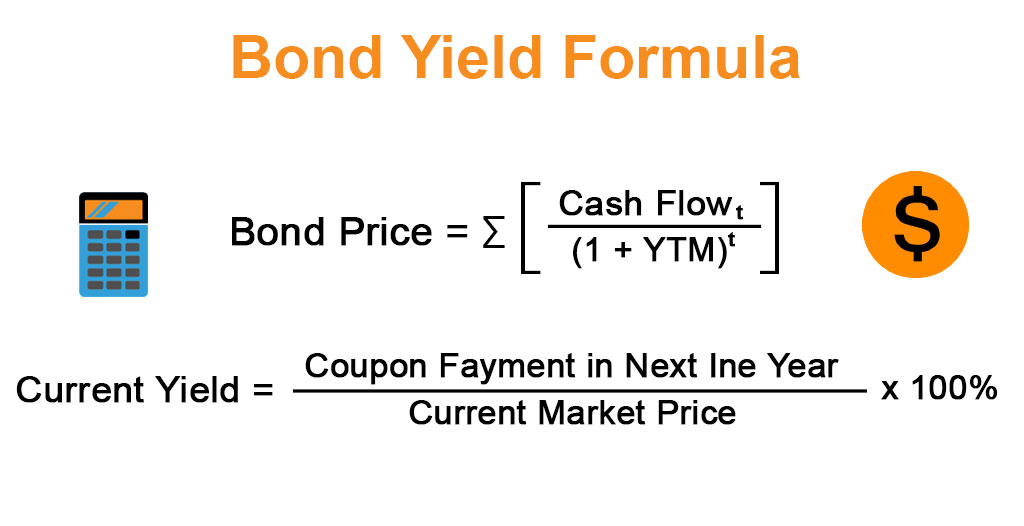


Bond Yield Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template


Q Tbn And9gcsp25zjynanfjklb7g 0opdrwusuwkhwdwzqpddk9o Usqp Cau
Therefore, if the 5Year Treasury Yield becomes 4%, still the coupon rate will remain 5%, and ifTherefore, the current yield of the bond is (5% coupon x $100 par value) / $9592 market price = 521% To calculate YTM here, the cash flows must be determined first Every six months (semiThe discount rate, in this case, is known as the yield to maturity (YTM) We can calculate bond yields using the RATE function in Excel This feature takes care of the iterations and calculates the bond yield in one go Example Bond Yield An investor purchased a 5year 4% coupon bond with annual payments at a price of %
/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



Introduction To Finance Instructor Michael E Asamoah Ppt Download
Coupon is the annual interest rate paid to bondholders Yield is a measure of return based on coupon and purchase price Example XYZ 400% bonds are due OCT 1 28 If we purchase this bond at par () the coupon rate 400% would also be the YBonds with low coupon rates will have higher interest rate risk than bonds that have higher coupon rates For example, consider a bond with a coupon rate of 2% and another bond with a coupon rate of 4% Keeping all the features the same, bond with a 2% coupon rate will fall more than the bond with a 4% coupon rate Maturity affects interestTo calculate the current yield for a bond with a coupon yield of 45 percent trading at 103 ($1,030), divide 45 by 103 and multiply the total by 100 https//wwwinchargeorg/financialliteracy/basicsofbondsmaturity/ Category Trading Show All Coupons



Bond Pricing And Accrued Interest Illustrated With Examples



Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Calculations In Debt Mutual Fund Nippon India Mutual Fund
The price of a bond and its yield are inversely related for bonds with a given principal amount, time to maturity, and coupon rate The logic is as follows The issuer is going to pay preR = discount rate (the yield to maturity)



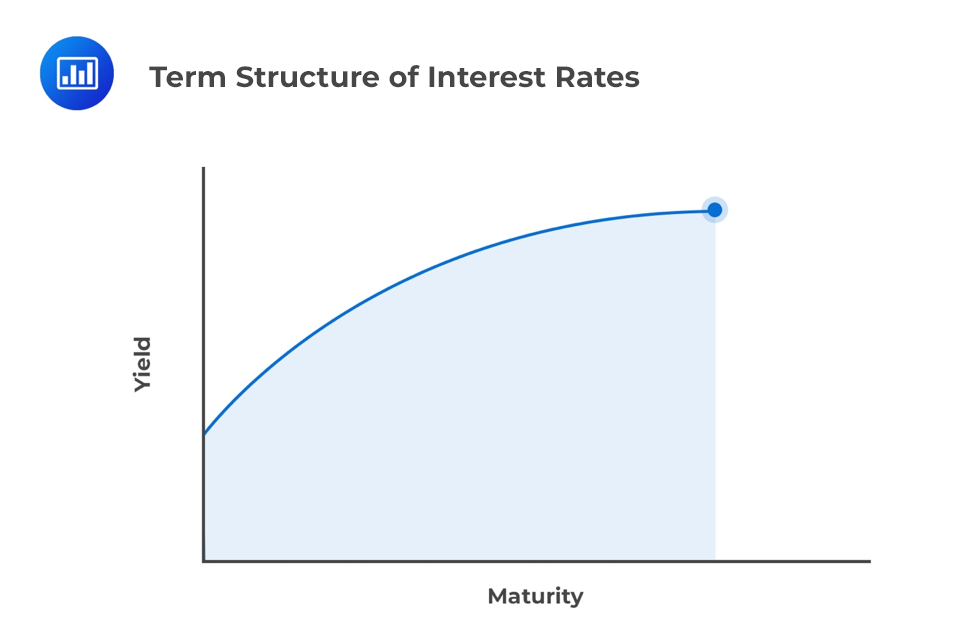
Yield Curve Wikipedia



Difference Between Yield To Maturity And Coupon Rate Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
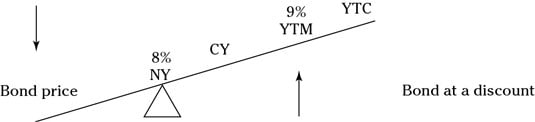


How To Calculate Bond Prices And Yields On The Series 7 Exam Dummies



Calculate The Coupon Rate Of A Bond Youtube



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox
%20will%20be%20priced%20to%20yield%20about%20the%20same%20return,%20regardless%20of%20the%20coupon%20rate..jpg)


Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator



Yield To Maturity Fixed Income



3 Valuing Bonds Ppt Video Online Download
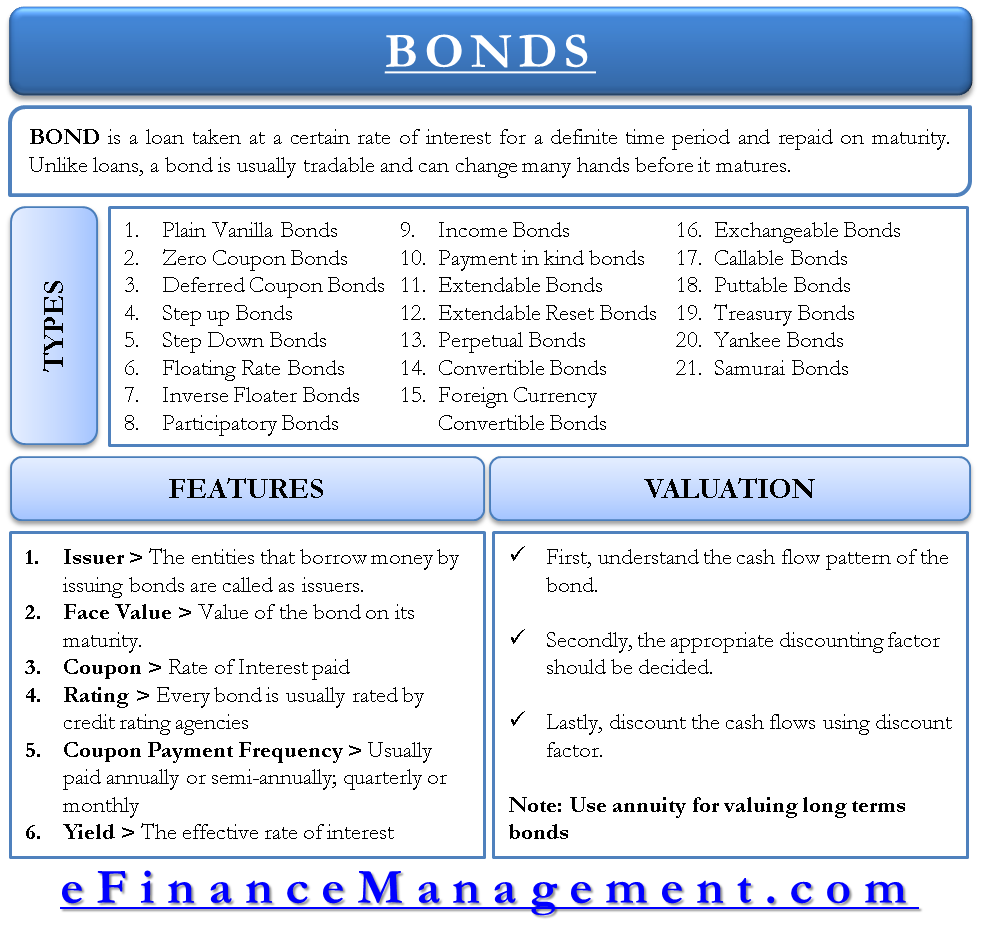


All The 21 Types Of Bonds General Features And Valuation Efm


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity


Duration Vs Maturity And Why The Difference Matters



Introduction To Bonds Fixed Income Security Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Bonds Fixed Maturity Exception Consols Which Never Mature Fixed Income From Periodic Interest Princi


Faculty Weatherhead Case Edu Ritchken Documents Chap 9 Pdf
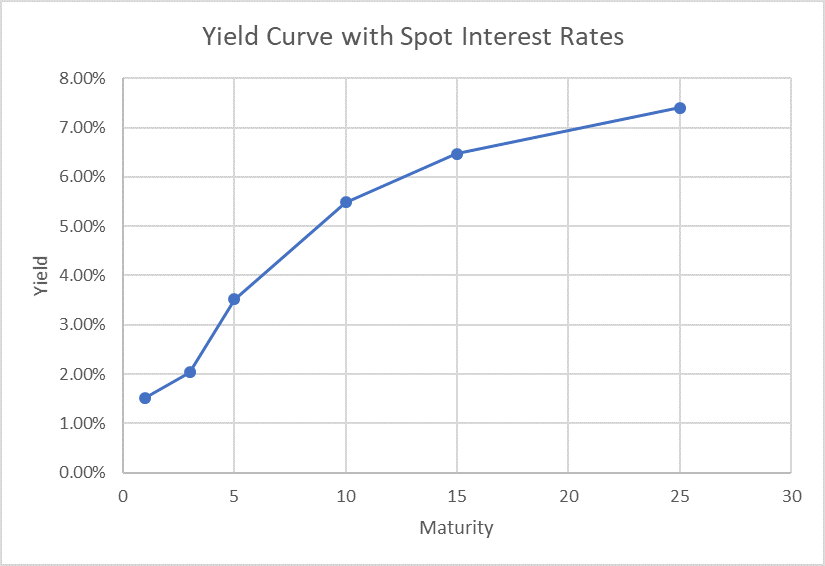


Spot Interest Rate Spot Curve And Yield To Maturity


Wwwfinance Bond Valuation Campbell R Harvey



Yield To Maturity Ytm And Yield To Call Ytc alectures Com
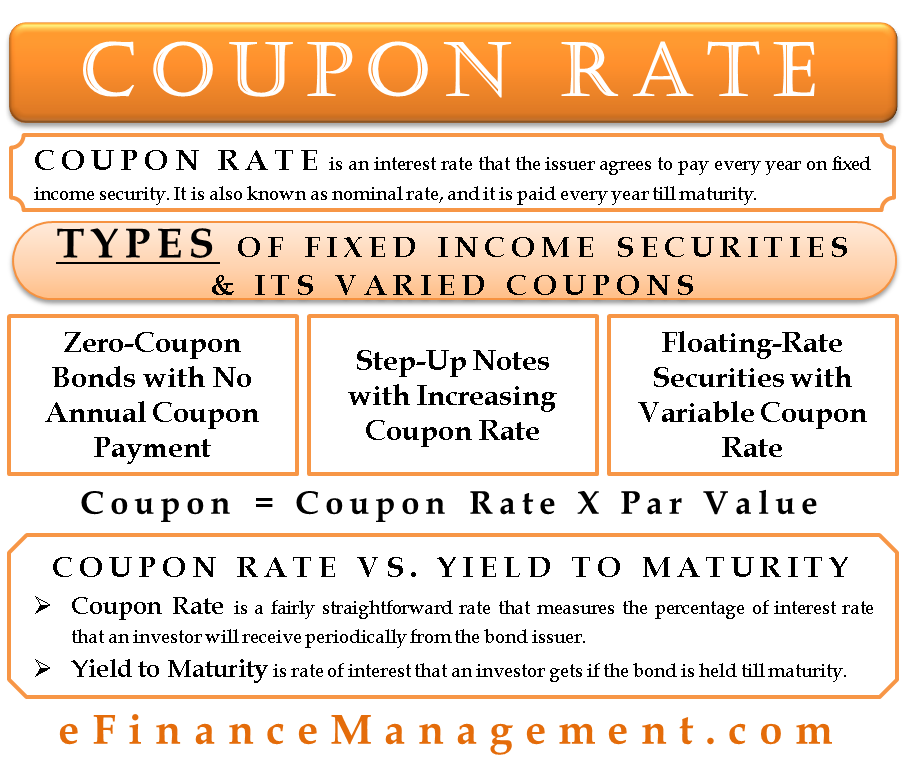


Coupon Rate Meaning Example Types Yield To Maturity Comparision
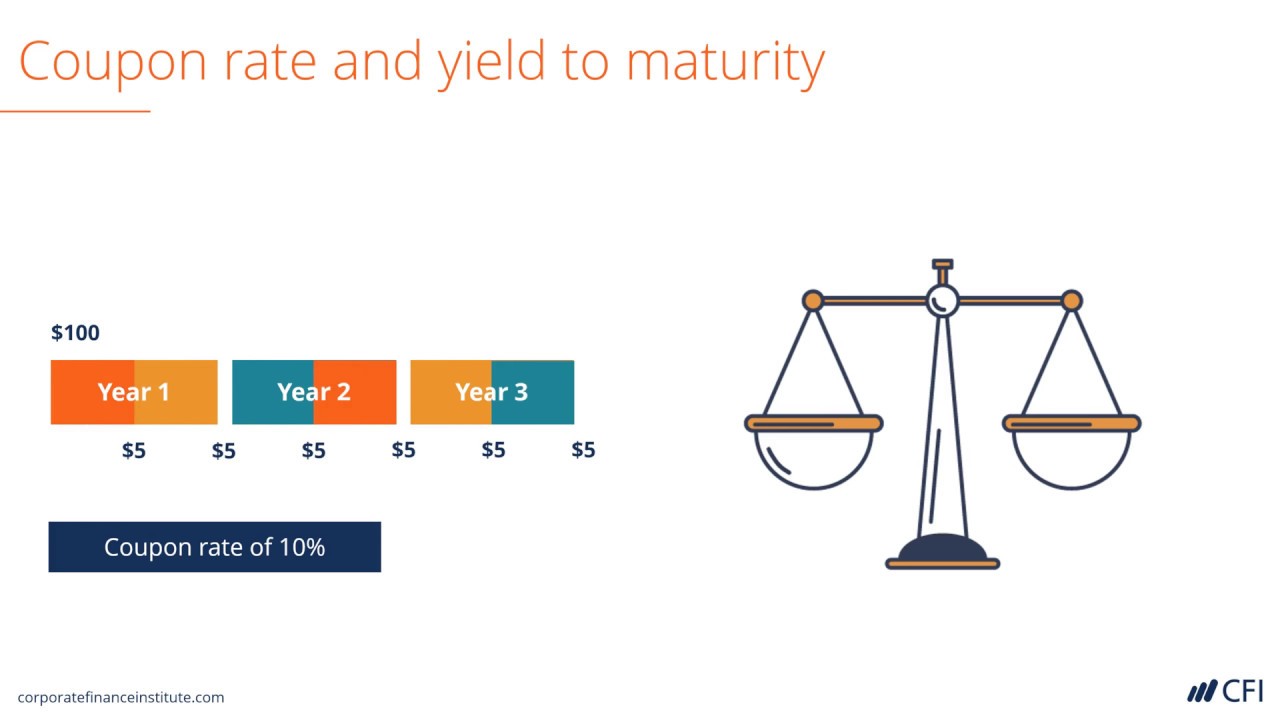


Coupon Rate And Yield To Maturity Youtube



Everything You Need To Know About Bonds Pimco



Relationship Between Bond Prices And Interest Rates Video Khan Academy


21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation
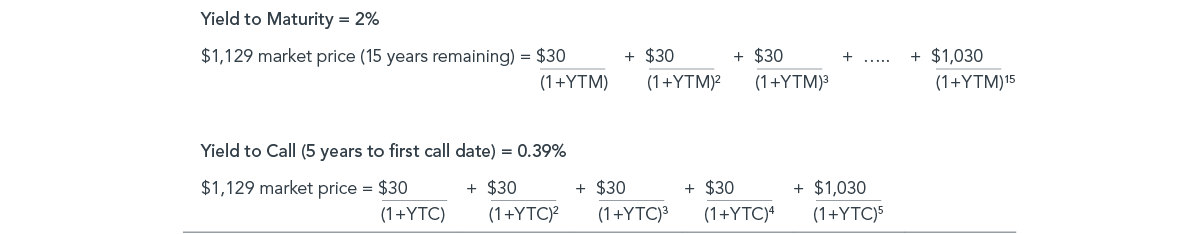


Considering Yield To Worst



Difference Between Yield To Maturity And Coupon Rate Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



1 Yield Curves For Danish Zero Coupon Bonds The Red Curve Is A Normal Download Scientific Diagram
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



Interest Rate Risk Of Bonds Full Valuation Approach Aka Scenario Analysis


Bond Prices Rates And Yields Fidelity


1



What Is The Difference Between Coupon And Yield Rate By Gulaq Medium



Premium Bonds 101 Breckinridge Capital Advisors
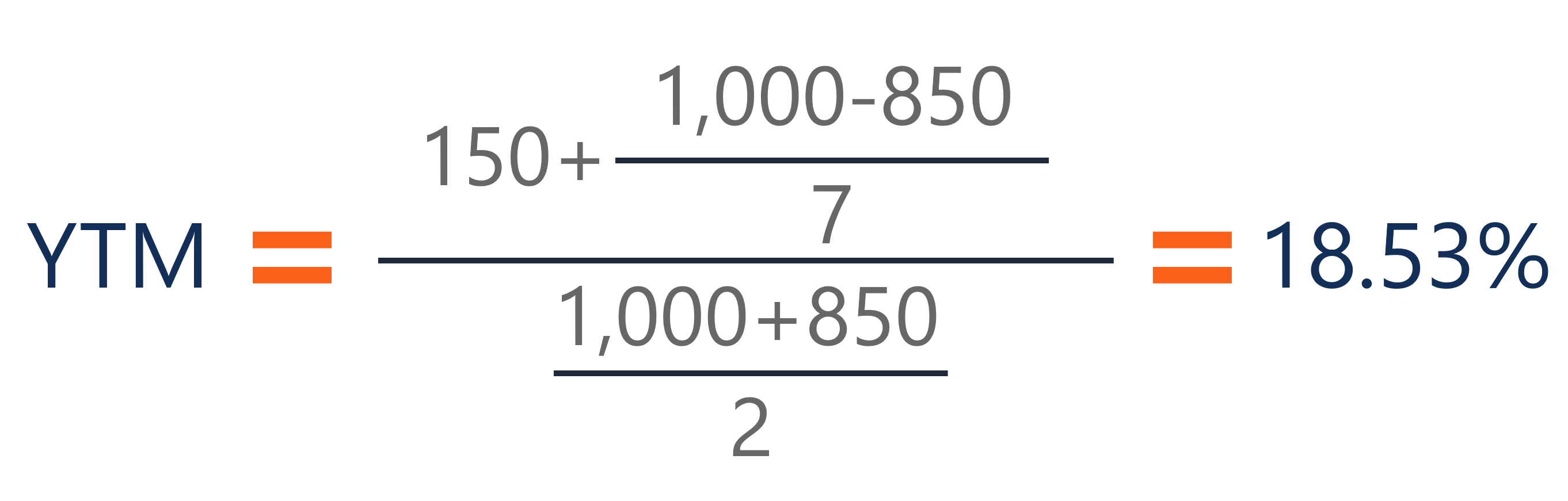


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel
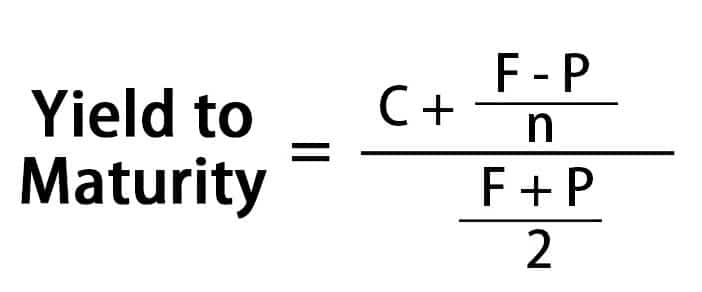


What Is The Approximated Yield To Maturity Ytm Forex Education



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond
/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



How To Calculate Bond Price In Excel


Www Iseg Ulisboa Pt Aquila Getfile Do Method Getfile Fileid



What Is Coupon Rate In Bonds Know More Fincash Com


Calculating Yield To Maturity Using The Bond Price


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel


P2tdoqhmnx Yjm


Coupon Vs Yield Top 5 Differences With Infographics
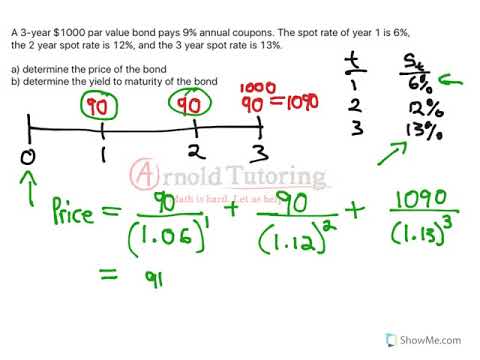


Bonds Spot Rates Vs Yield To Maturity Youtube
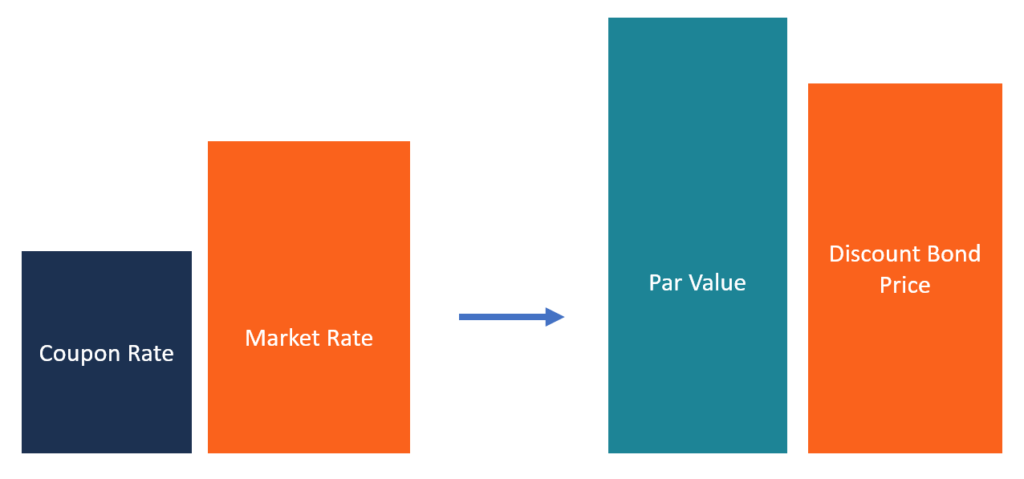


Discount Bond Bonds Issued At Lower Than Their Par Value


Fcondemand Fixed Income Investing
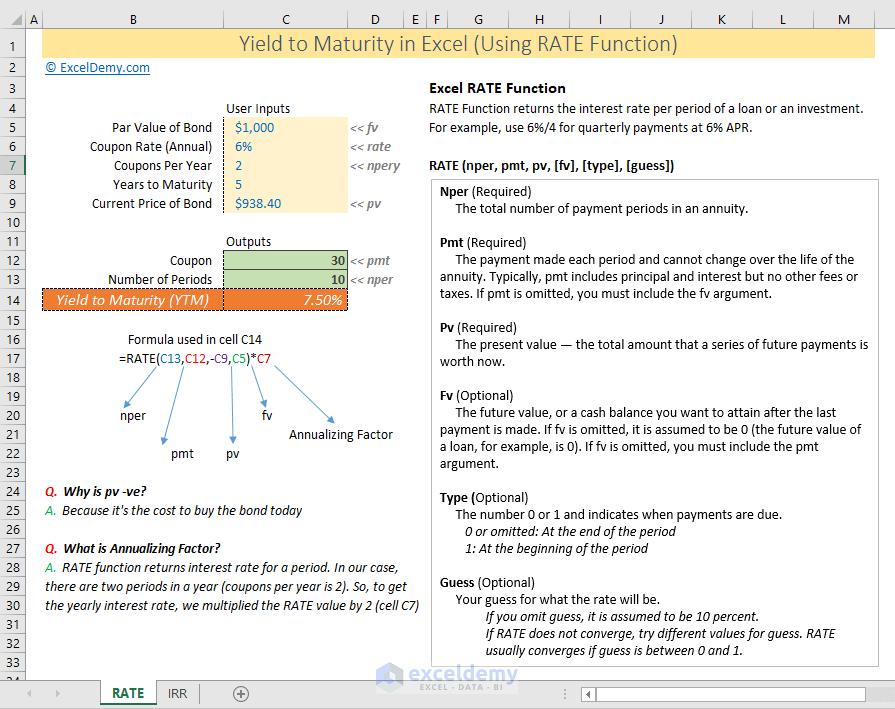


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy
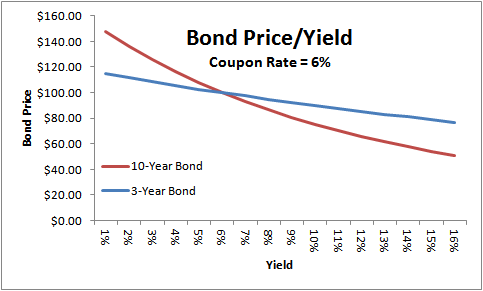


Bond Yields Nominal And Current Yield Yield To Maturity Ytm With Formulas And Examples
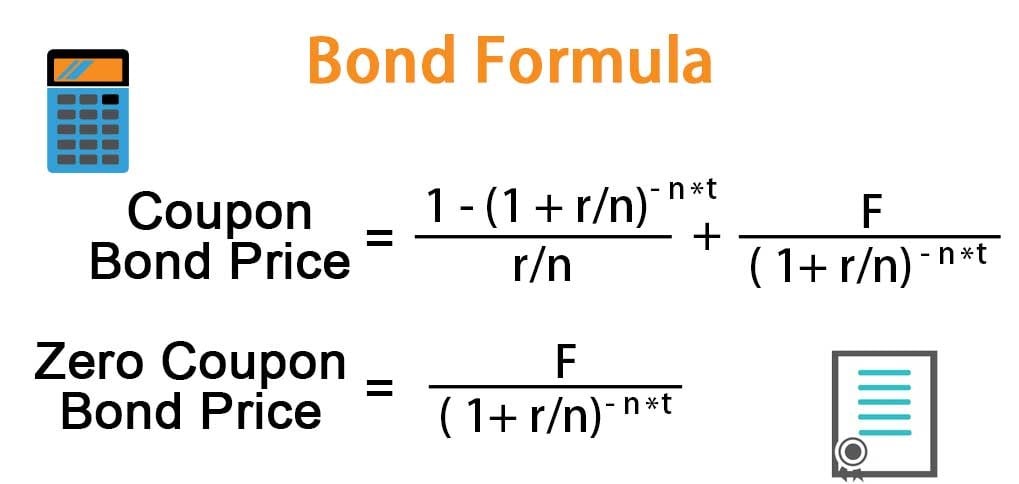


Bond Formula How To Calculate A Bond Examples With Excel Template


Skb Skku Edu Summer Board Academic Do Mode Download Articleno 293 Attachno
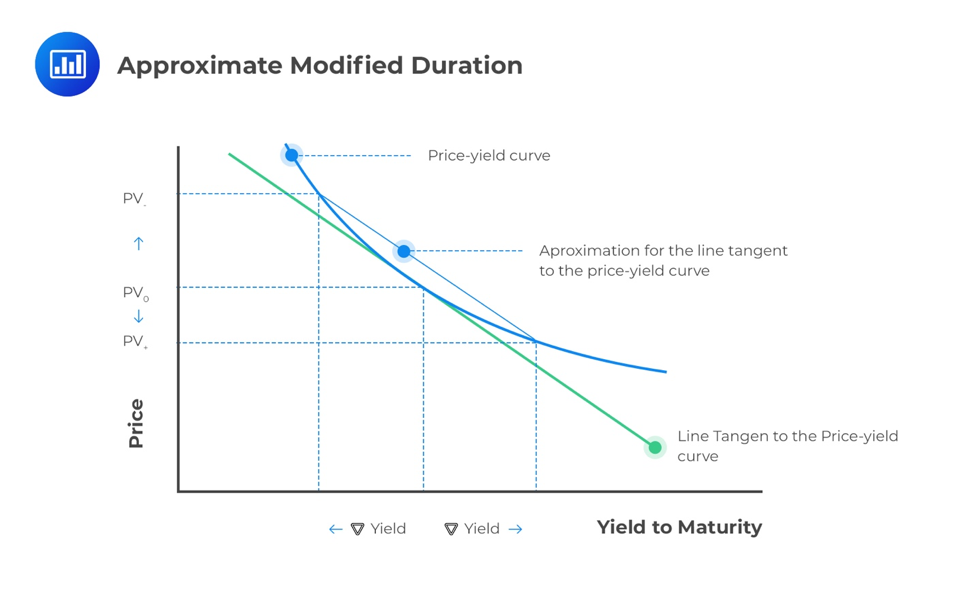


Macaulay Modified And Effective Durations Cfa Level 1 Analystprep



Bond Economics Primer Par And Zero Coupon Yield Curves



Zero Coupon Bond Definition Formula Examples Calculations
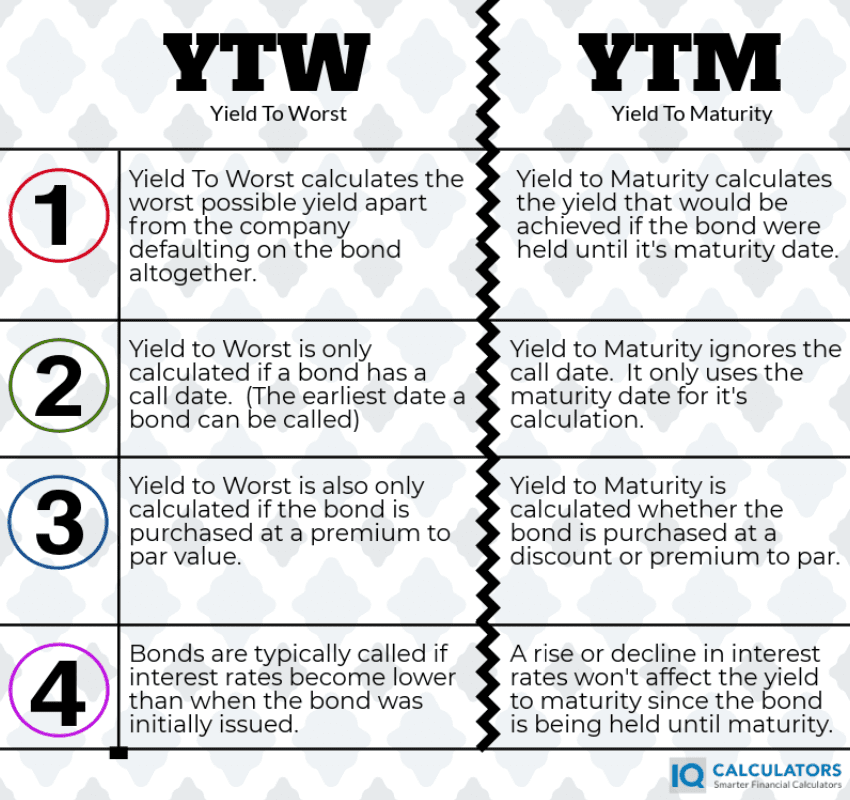


Yield To Worst What It Is And Why It S Important



Bond Yield Calculator
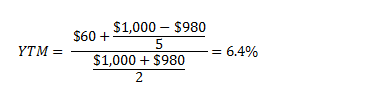


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool
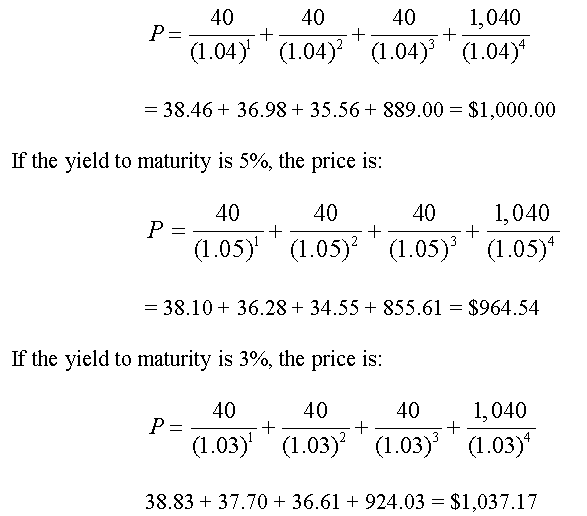


An Introduction To Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Pricing



Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
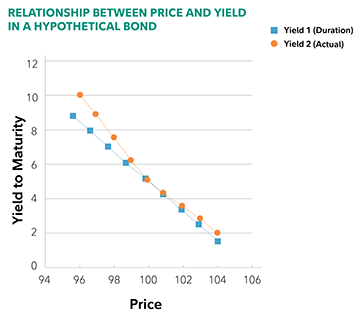


Duration Understanding The Relationship Between Bond Prices And Interest Rates Fidelity



How To Use The Excel Yield Function Exceljet
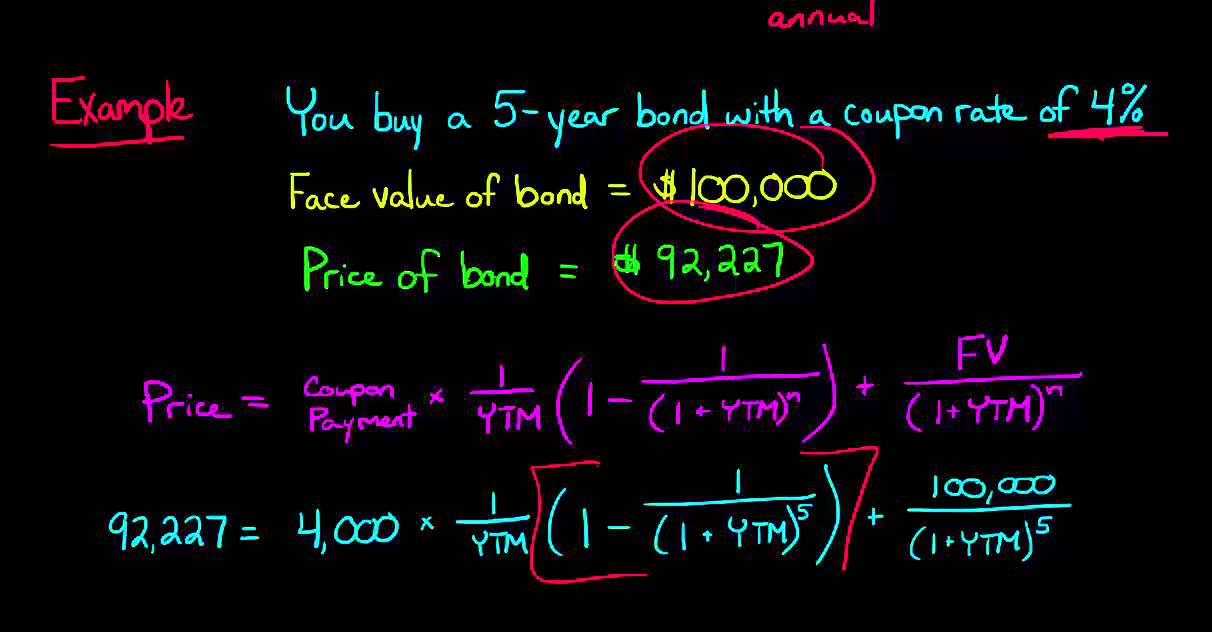


Calculating The Yield Of A Coupon Bond Using Excel Youtube



Chapter 4 Valuation And Bond Analysis Business Finance Essentials


Q Tbn And9gctgci569w 7oknoisht4 L Qoklxjxlzb1hfddepfxrk3ogx8u3 Usqp Cau
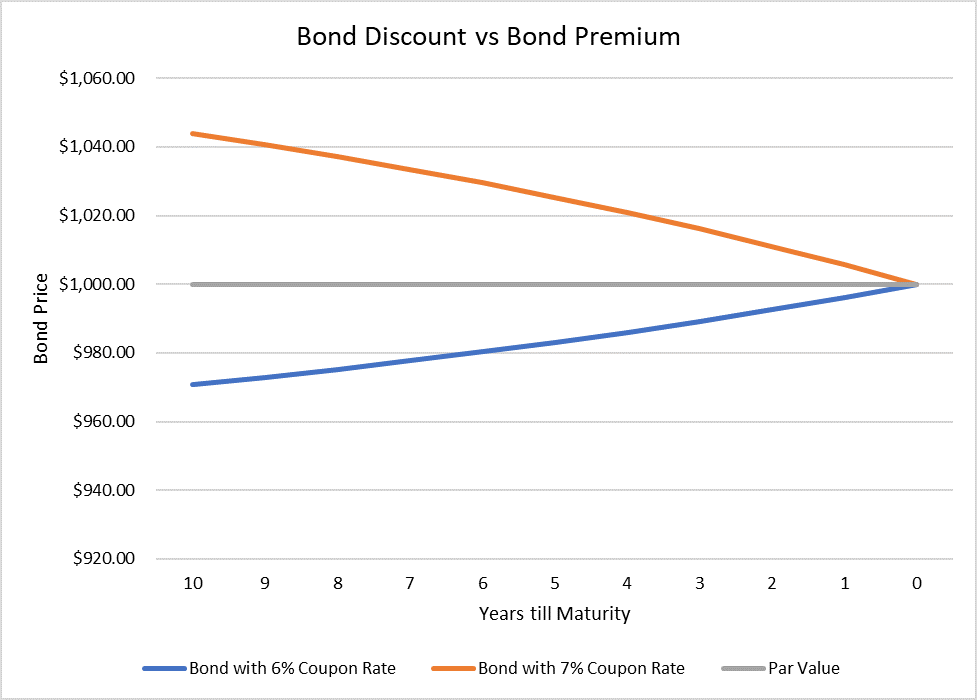


Bond Discount And Premium Calculation Example
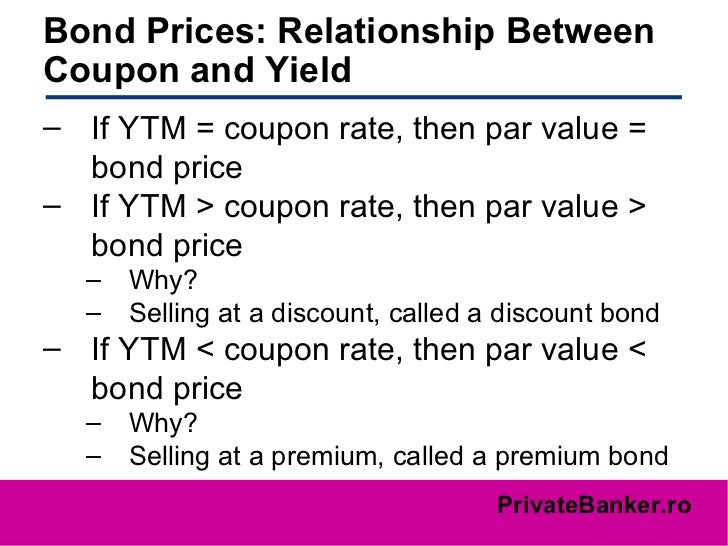


Bond Valuation


Faculty Weatherhead Case Edu Ritchken Documents Chap 9 Pdf
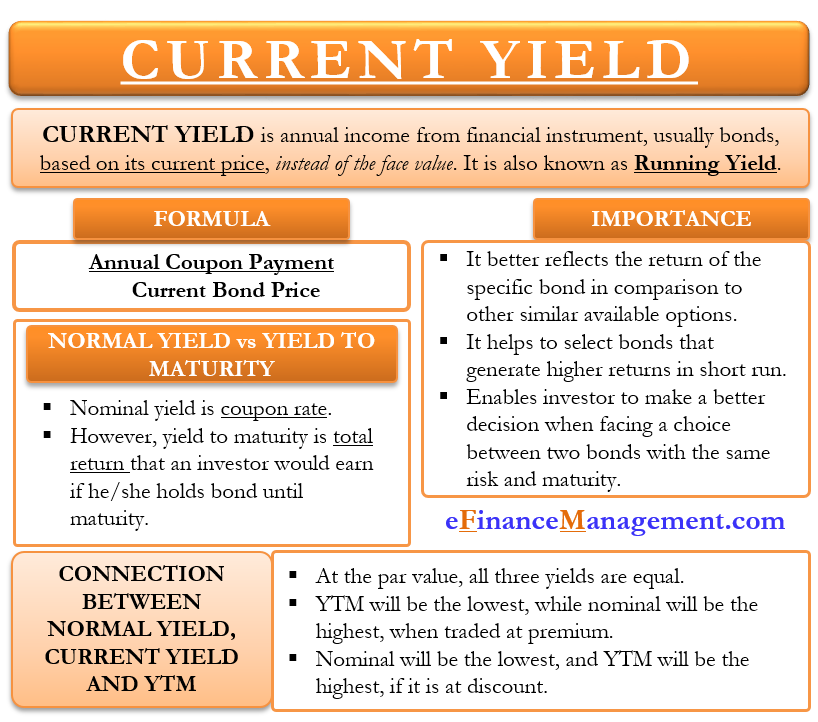


Current Yield Meaning Importance Formula And More
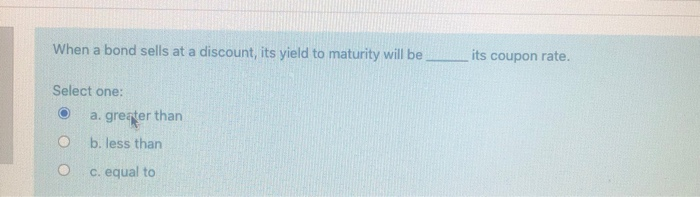


Solved When A Bond Sells At A Discount Its Yield To Matu Chegg Com



Coupon Rate Definition And Meaning Market Business News



How To Calculate The Rate Of Return On A Coupon Bond Youtube



21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation



Bonds Yields And Yield To Maturity Economics Online


What Is The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond With A Face Value Of 1 000 Current Price Of 0 And Maturity Of 4 0 Years Recall That The Compounding Interval


Q Tbn And9gcsk2iegdz1jvuavgo487nzmoaxjpygzrxk8ljgamhuz Bsed74b Usqp Cau
/female-executive-talking-to-colleagues-117455512-5750d4d75f9b5892e8b3d3af.jpg)


Important Differences Between Coupon And Yield To Maturity


Skb Skku Edu Summer Board Academic Do Mode Download Articleno 293 Attachno
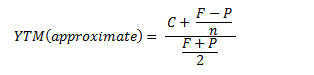


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool


コメント
コメントを投稿